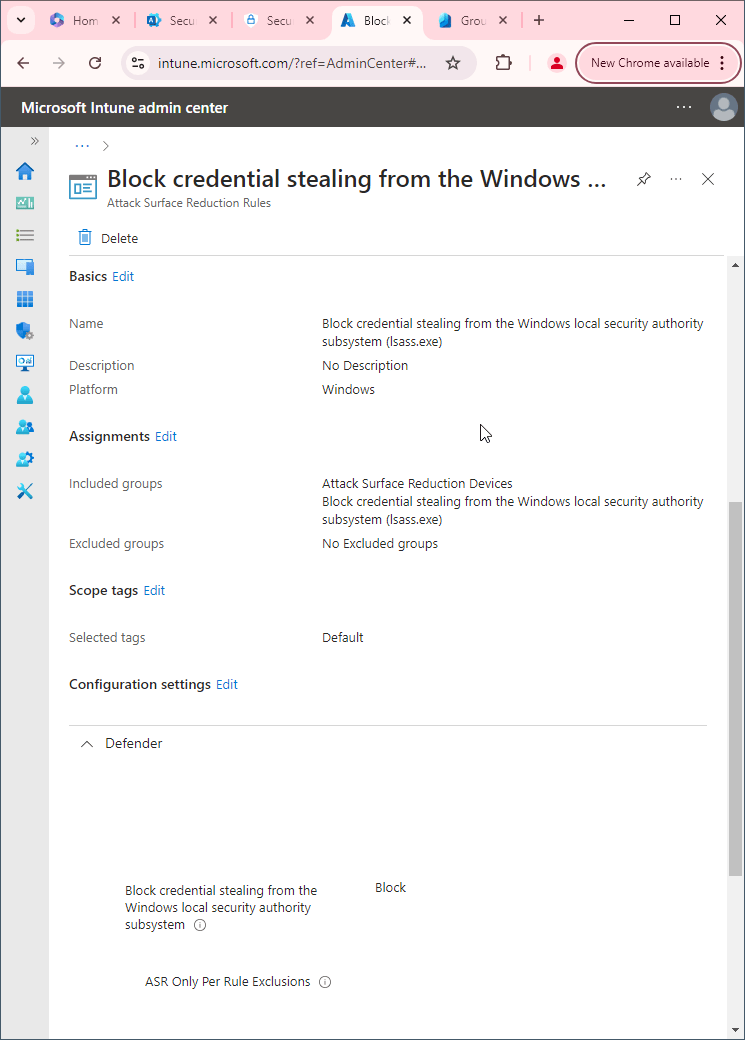
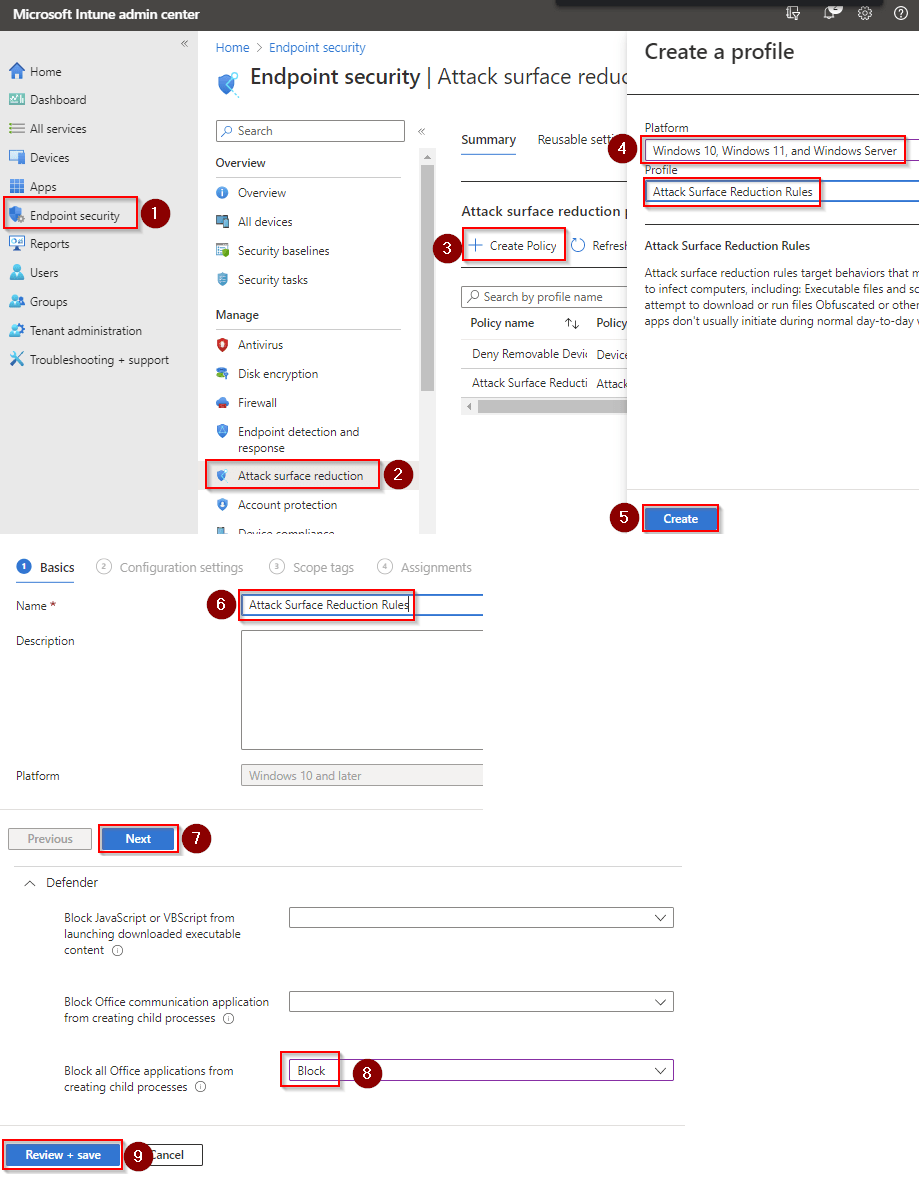
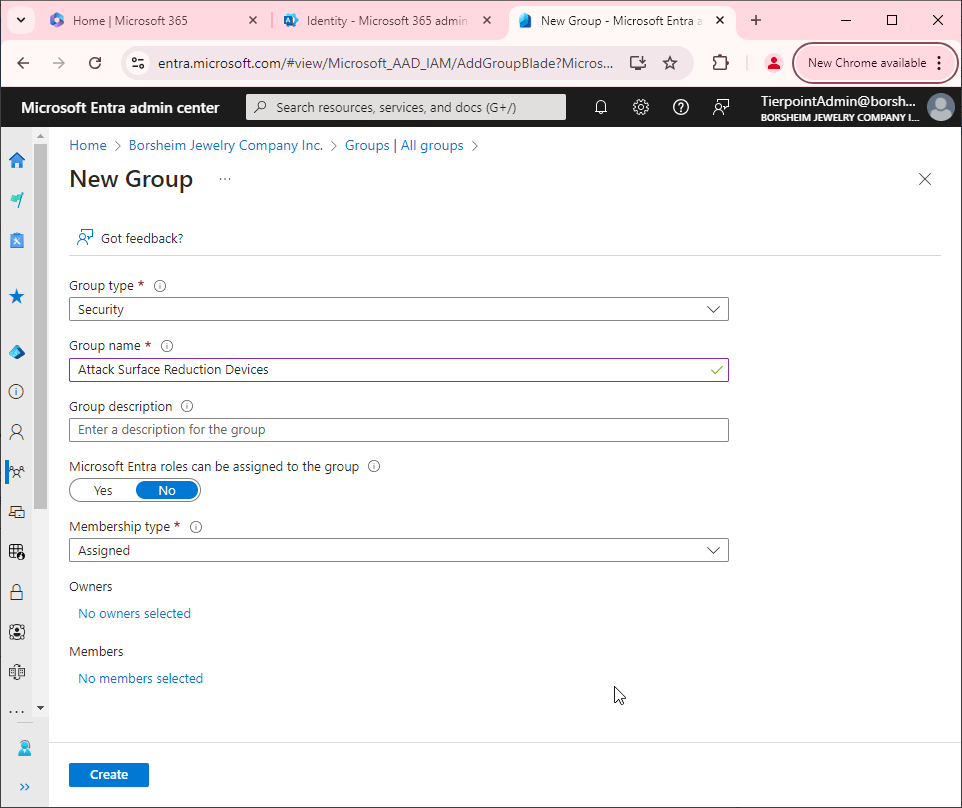
13 Microsoft 365 Admin accounts best practices
It goes without saying that the admin accounts are the most important accounts to protect. They require extra safeguards because if someone gains access to an admin account, they can... Do anything an admin can do in your tenant. Anyway, let's jump into the 15 safeguards I recommend you should at least know about.
- Use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Enforce MFA for all admin accounts to add an extra layer of security.
- Assign Least Privilege Access: Follow the principle of least privilege by granting admin rights only to those who absolutely need them. Use role-based access control (RBAC) to assign specific roles rather than broad admin access.
- Use Dedicated Admin Accounts: Create separate admin accounts for administrative tasks, avoiding using standard user accounts for admin purposes.
- Enable Security Defaults: Utilize Microsoft 365's security defaults to enhance baseline security settings automatically.
- Regularly Review Admin Roles and Permissions: Conduct periodic reviews of admin roles and permissions to ensure they are up-to-date and aligned with current needs.
- Implement Conditional Access Policies: Set up conditional access policies to control how and when admin accounts can access Microsoft 365 resources.
- Monitor and Audit Admin Activities: Enable auditing and regularly review logs to monitor admin activities and detect any suspicious actions.
- Use Privileged Identity Management (PIM): Use PIM to manage, control, and monitor access to important resources in Microsoft 365.
- Regularly Update and Patch Systems: Ensure that all systems and software used by admin accounts are regularly updated and patched.
- Educate and Train Admins: Provide ongoing training for admins on security best practices, emerging threats, and new Microsoft 365 features.
- Implement Strong Password Policies: Enforce strong password policies, including regular password changes and the use of complex passwords.
- Use Secure Devices: Ensure that devices used by admins are secure, with up-to-date antivirus software and encrypted storage.
- Limit Admin Sign-In Locations: Restrict admin sign-ins to trusted locations or devices to reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
1. Use MFA
Multi-factor authentication is a no brainer. All of your users should be using it. It's especially important for your admins to be using it. There are a number of ways to setup MFA so I'll just link The many ways to implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) in Microsoft 365.
2. Least Privilege Access
This is another no brainer. Why give someone global admin access if all they need to do is create new users? Of course, if you're a smaller company you might only have a couple of admins and therefore, they all should be global admins but as a rule of thumb, no more than 5 global admin accounts. You can learn about setting about admins at Creating and managing admins through roles.
3. Use Dedicated Admin Accounts
This one is not so obvious so let me explain. What happens when you fall for a phishing email? You get the email, click the link, enter your credentials, right? Well, what happens when one of your admins fall for a phishing email? They give up their credentials. Do you want the malicious actor to have admin credentials or standard user credentials? So, every admin should have two accounts. One, there standard user account that has a license and everything. Two, there admin account. You can name the admin account anything. John.Admin@gitbit.org. Admin.John@gitbit.org. GruberA@gitbit.org admin-Gruber@gitbit.org. The list goes on and on.
4. Enable Security Defaults
Security defaults is a way to secure your Microsoft 365 tenant without configuring all the pieces. For example, security defaults automatically enable MFA. Security defaults can't be turned on if you use conditional access policies so if you're using conditional access policies you might want to manually setup the conditional access policies to match the security defaults. Here's what security defaults does:
- Requiring all users to register for multifactor authentication
- Requiring administrators to do multifactor authentication
- Requiring users to do multifactor authentication when necessary
- Blocking legacy authentication protocols
- Protecting privileged activities like access to the Azure portal
5. Regularly Review Admin Roles and Permissions
We'd all like to think we and our teams never forget anything but it happens all the time.